6278. City
numbers
As you may be
aware, houses with even street numbers are typically situated on one side of
the street, while those with odd numbers are positioned on the opposite side. Determine whether the houses numbered n and m are situated
on the same side of the street.
Input. Two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 100).
Output. Print 1 if the houses with numbers n and m are
located on the same side of the street, and 0 otherwise.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
1 2 |
0 |
SOLUTION
conditional
statement
Algorithm analysis
Two houses are on the same side of the street if their numbers are both odd
or both even.
·
If the sum of the numbers n + m
is even, then n and m have the same parity.
·
If the sum of the numbers n + m
is odd, then n and m have different parities.
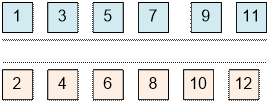
The condition for checking whether n
and m have the same parity can be expressed as:
if ((n is even and m is even)
|| (n is odd and m is odd))
This can be
simplified to:
if ((n + m) % 2 == 0)
Algorithm
implementation
Read the input data.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
If the sum of the numbers n + m is even, then n and m have the same parity. In this case print
1. Otherwise print 0.
if ((n + m) % 2 == 0) puts("1");
else puts("0");
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String []args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int m = con.nextInt();
if ((n + m) % 2 == 0)
System.out.println("1");
else
System.out.println("0");
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the input data.
n, m = map(int, input().split())
If the sum of the numbers n + m is even, then n and m have the same parity. In this case print
1. Otherwise print 0.
if (n + m) % 2 == 0:
print("1")
else:
print("0")